Neurological diseases
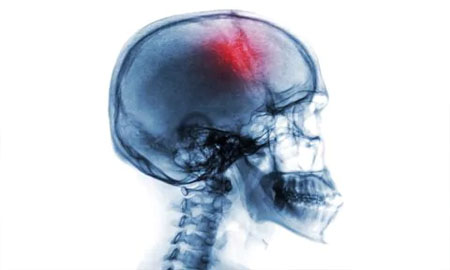
Stroke
The sudden death of brain cells due to lack of oxygen, caused by blockage of blood flow or rupture of an artery to the brain. Sudden loss of speech, weakness, or paralysis of one side of the body can be symptoms. ... Also known as cerebrovascular accident.
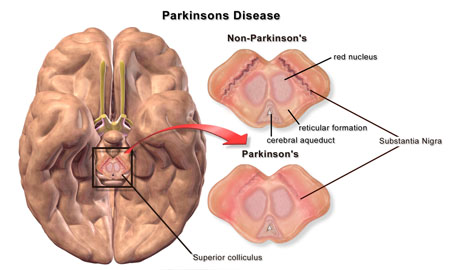
Parkinsonism
Definition of Parkinson's disease. : a chronic progressive neurological disease chiefly of later life that is linked to decreased dopamine production in the substantia nigra and is marked especially by tremor of resting muscles, rigidity, slowness of movement, impaired balance, and a shuffling gait.

Dementia
Dementia is not a specific disease. It's an overall term that describes a group of symptoms associated with a decline in memory or other thinking skills severe enough to reduce a person's ability to perform everyday activities. Alzheimer's disease accounts for 60 to 80 percent of cases.
Chronic Migraine
Chronic migraine is a distinct and relatively recently defined sub-type of Chronic Daily Headache. The International Headache Society defines chronic migraine as more than fifteen headache days per month over a three month period of which more than eight are migrainous, in the absence of medication over use.
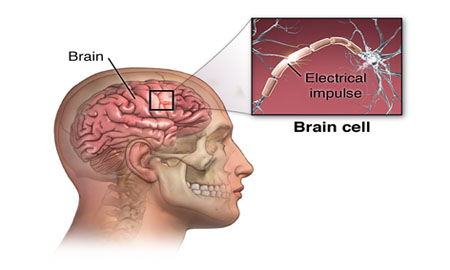
Seizures
Seizure disorders: One of a great many medical conditions that are characterized by episodes of uncontrolled electrical activity in the brain (seizures). Some seizure disorders are hereditary, but others are caused by birth defects or environmental hazards, such as lead poisoning.
Spinal Cord Diseases
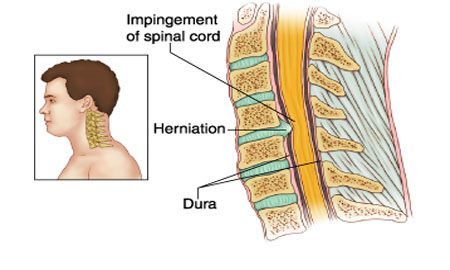
Myelopathy
Myelopathy is a disorder that results from severe compression of the spinal cord. ... Causes of myelopathy include spinal stenosis, spinal trauma and spinal infections, as well as autoimmune, oncological, neurological and congenital disorders.
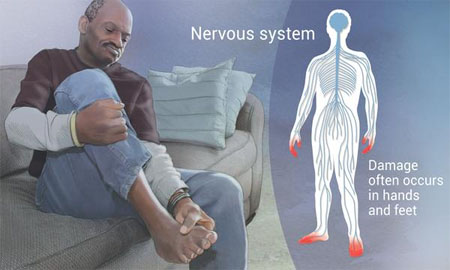
Peripheral Neuropathy
A common cause of peripheral neuropathy is diabetes, but it can also result from injuries, infections and exposure to toxins. Treatments include antidepressants such as amitriptyline, pain medication such as oxycodone, anti-seizure medication and pain-relieving creams. It's also important to treat the underlying condition.
Muscle Disease
Muscular dystrophy is a group of diseases that cause progressive weakness and loss of muscle mass. In muscular dystrophy, abnormal genes (mutations) interfere with the production of proteins needed to form healthy muscle.

Myasthenia
The condition is caused by a breakdown in communication between nerves and muscles. Symptoms include weakness in the arm and leg muscles, double vision and difficulties with speech and chewing. Medication, therapy and surgery can help.
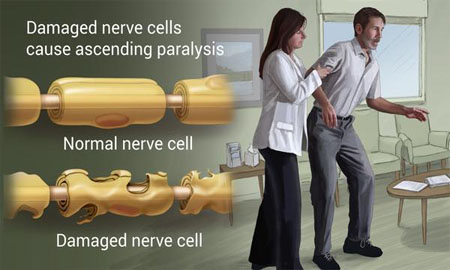
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
The condition may be triggered by an acute bacterial or viral infection. Symptoms start as weakness and tingling in the feet and legs that spread to the upper body. Paralysis can occur. Special blood treatments can relieve symptoms. Physiotherapy is required.
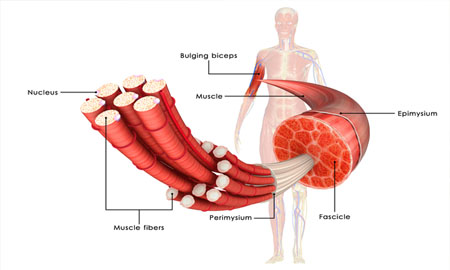
Periodic Paralysis
Periodic paralysis (also known as myoplegia paroxysmalis familiaris) is a group of rare genetic diseases that lead to weakness or paralysis from common triggers such as cold, heat, high carbohydrate meals, not eating, stress or excitement and physical activity of any kind.
Demyelinating diseases
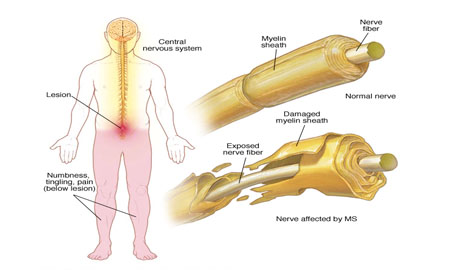
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis causes many different symptoms, including vision loss, pain, fatigue and impaired coordination. The symptoms, severity and duration can vary from person to person. Some people may be symptom free for most of their lives, while others can have severe, chronic symptoms that never go away.
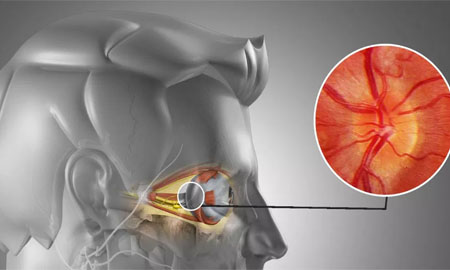
Optic Neuritis
Optic neuritis is often associated with multiple sclerosis and can be an early sign of the disease. Pain and temporary vision loss are common symptoms. Optic neuritis usually gets better on its own. In some cases, steroid medications are used to reduce inflammation.
Disorders

Sleep disorders
Sleep disorders are changes in the way that you sleep. A sleep disorder can affect your overall health, safety and quality of life. ... Insomnia, in which you have difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep throughout the night. Sleep apnea, in which you experience abnormal patterns in breathing while you are asleep.
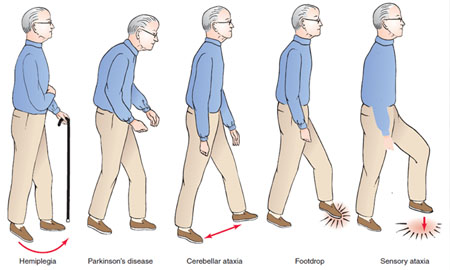
Gait disorders
Gait abnormality is a deviation from normal walking (gait). Watching a patient walk is the most important part of the neurological examination. Normal gait requires that many systems, including strength, sensation and coordination, function in an integrated fashion.
All neonatal and paediatric patients are also being treated here
neonatal
Neonatal: Pertaining to the newborn period, specifically the first 4 weeks after birth.
paediatric
Pediatrics is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, and adolescents.